SEO Trends in 2026: What’s Changing and How to Stay Ahead
In 2026, SEO trends are changing faster than most teams expected. The changes don’t feel like a big overhaul; they feel more like a quiet change in how people find reliable information online. Search engines are putting more weight on context and intent. They reward pages that read naturally and seem likely to help, rather than those made to look good. AI content is everywhere, so human insight is what really sets you apart, especially when it comes to topics that need clarity or personal experience. Visual, voice, and multi-modal search are becoming part of our daily lives, which is making websites think beyond just text. As privacy rules get stricter, relying on solid first-party data is starting to feel less like a choice and more like a skill you need to survive. It can be hard to figure all of this out, but staying curious and making changes early makes things a lot less stressful.
Want to stay on top of the latest SEO trends in 2026? Read the comprehensive guide and start improving your strategy right away.
What Are the Key SEO Trends Shaping 2026?
In 2026, search engine optimization seems less like trying to figure out how search engines work and more like keeping up with how people really search. As search engines get better at figuring out what people want, sites that answer real questions in a clear, simple way tend to gain trust faster. People are also using visual search more and more. They take a picture or do a quick scan and expect results right away that are correct. At the same time, AI-generated content is everywhere, so being real and having firsthand experience is more important than ever. It’s almost like a quiet filter that people use before they believe anything. Technical performance still affects rankings, but now the focus is on consistency and reliability instead of getting small speed boosts. And because privacy updates are always coming out, keyword data is less reliable. This means that brands need to get to know their customers better instead of just looking at numbers.
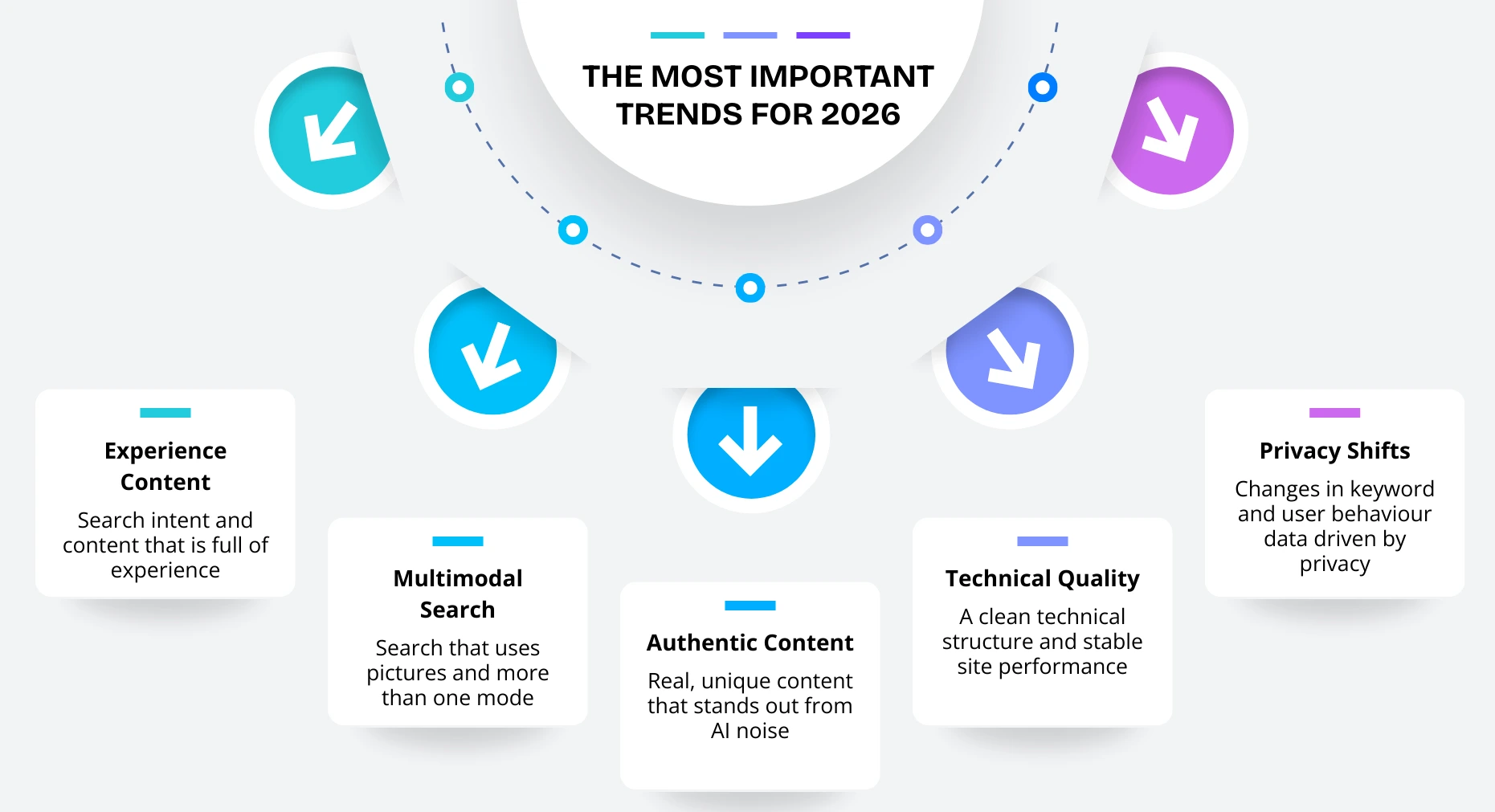
The Most Important Trends for 2026
- Search intent and content that is full of experience
- Search that uses pictures and more than one mode
- Real, unique content that stands out from AI noise
- A clean technical structure and stable site performance
- Changes in keyword and user behavior data driven by privacy
Why SEO Is Evolving Faster Than Ever
Search engines are no longer static; they are always moving, which is changing how websites get noticed. Algorithms change faster than most teams can write about them, and so do the ways people use them. One week, people skim, and the next, they want more detailed answers. With AI-generated content taking over the web, quality signals suddenly matter more than they did a few years ago. Brands need to think about more than just keywords because search is getting more conversational and aware of context. Things that worked last year may seem strange and out of date today. This fast pace keeps marketers curious rather than relying on old playbooks. Sometimes things get a little messy, but that’s what keeps SEO alive and surprisingly exciting. Websites also need to rethink how they present information, given new formats such as AI overviews and interactive results. As search engines keep mixing technology with what people really want, being able to adapt is becoming the most important SEO skill.
How User Search Behavior Is Changing in 2026

[1] More and More People are Comfortable with Voice-First Searches
Voice searches will keep growing in 2026 as more and more people prefer to ask questions naturally instead of typing. A lot of people use voice when they are doing more than one thing at once or when they just don’t want to deal with a keyboard. This change pushes brands to give clearer, easier-to-understand answers, like how people talk in real life.
[2] Visual Search Is Now a Daily Habit
Taking a picture to get information is becoming second nature, especially for younger users who think in pictures before they speak. It fixes the “I don’t know what this is called” problem and makes it easier to find products. Users expect quick recognition and accurate suggestions from visual search, not a long list of items that aren’t very related.
[3] The Rise of Very Specific “Micro Queries.”
People are moving away from broad searches and towards more specific, detailed queries that show exactly what they want. They don’t just ask for “best laptop”; they ask for very specific features or situations. This change makes websites give clear, simple answers that don’t use jargon and really answer the question instead of dancing around it.
[4] AI Assistants Changing the Way We Find Things
Users like the personalised, context-aware answers that AI assistants give, so more searches now start there than in traditional search engines. These helpers use your past actions and preferences to make it easier to find useful information. Because of this, users want answers that feel personal without having to change the query themselves.
[5] More Specific Local Needs and Needs in Real Time
People are starting to do more local searches that are more useful and urgent. They are looking for things that are available, when they are available, and how close they are. People want to know what’s available, what’s in stock, and how quickly they can get it. Companies that keep their information up to date in real time tend to gain trust faster and seem more relevant.
[6] People Want Signals of Trust and Authenticity
Users don’t skim as much, but they do evaluate more, paying more attention to tone, openness, and real-world proof before clicking. They don’t like content that is too polished or generic, and they prefer pages that feel real and grounded. Clear sources, real language, and obvious signs of credibility are now very important for how people search.
How AI Search and Google’s AI Overviews Are Transforming SEO
The search landscape had changed a lot by the start of 2025. People began to use Google’s AI Overviews (GEO) for everyday searches, and they realised that they were using conversational summaries more than long result pages. Traditional SEO was still important, but it had to compete with AI search behaviors that value usefulness, structure, and clarity.
[1] GEO Changes the Meaning of “Visibility”
Generative Engine Optimization often answers the user right away, so ranking isn’t just about who is at the top of the blue links anymore. Summaries often link to pages that have clear, useful explanations. This brings in more intentional visitors instead of just curious ones. This makes SEO visibility quieter but more important.
[2] AEO Tells Creators to Answer Questions Directly
Answer Engine Optimization tells pages to write answers in a way that AI search engines can understand without getting confused. AI can tell who is really in charge by using simple language, clear definitions, and well-documented steps. It’s not so much about writing longer posts as it is about getting rid of things that make it hard for AI to understand what you’re saying.
[3] AI Search Gives Points to Content That Has Real-World Connections
AI Overviews use a lot of sources that sound like they come from real life and not like they were copied from a template. GEO thinks that content is more real when it has small details, examples, or even small mistakes. That honesty often makes AI search bring it up higher in follow-up prompts.
[4] Structured Data Acts as a Translator for AI Systems
Schema markup and clean metadata help GEO figure out what a page is really trying to say. AI can easily find product specs, steps, or local details instead of having to guess what they are. This lowers the chance of misunderstandings and gives the page a better chance of being included in summary-style results or cited.
[5] Engagement Metrics are More Important Than Ever
After a user clicks on the GEO summary, AI systems keep track of how long they stay, whether they scroll, and whether the information actually answers their question. Pages that are calmer, have fewer interruptions, and are easier to navigate naturally keep visitors. These small changes to usability can make SEO work better.
[6] Search Queries That Sound Like Conversations Change Keyword Strategy
Search terms got longer and sounded more natural by the end of 2025. AI search engines get questions about edge cases, messy situations, and very specific situations. Sites that go into more detail instead of just giving a general overview tend to do better in search results, especially when GEO shapes the follow-up questions.
[7] Structured Data is the Quiet Backbone of SEO and AEO
Schema markup and clean metadata help AI understand what’s important by tagging things like prices, instructions, and product variations. GEO uses these cues to make sure it doesn’t get the context wrong. Pages that keep their structured data consistent often look more trustworthy to both traditional SEO metrics and AEO frameworks.
[8] SEO is Getting Closer to Being Honest by 2026
GEO is giving more and more weight to pages that sound like they were written by a real person who knows what they’re talking about, not a machine trying to impress another machine. AI is more likely to trust content that has small mistakes, clear explanations, and open reasoning. This change makes the difference between SEO done for algorithms and SEO done for real people looking for answers even bigger. People are now very concerned about how credible things are when they search.
What Google AI Overviews Mean for Organic Traffic
Google’s AI Overviews have changed the search results in a way that makes it seem like someone moved everything in your living room overnight. Everything is still there, but it’s not where it used to be. Websites that used to get steady organic traffic are now seeing more unpredictable patterns, especially when Google gives the gist of the answer right away. Some pages still get clicks when they offer more information or a clear next step, but thinner content has a hard time competing with a summary that is already in the results. Visibility can go up one week and down the next, which makes for a strange mix of opportunity and anxiety. Sites that have useful, well-organised information tend to show up more often, while sites that are full of filler paragraphs and keyword stuffing get pushed to the back. Instead of chasing after small ranking tricks, the change pushes everyone towards content that really solves a problem or adds a new layer that the overview can’t show.
How to Optimize Content for Inclusion in AI Overviews
[1] Start With Clear, Simple Answers
AI Overviews usually show pages that give searchers what they want without making them look for it. AI systems can understand the main point better when there are short, steady explanations at the top of the page. The rest of the content can then naturally go into more detail. AI models often agree with readers when they say the page “gets to the point.”
[2] Don’t Make Sentences Too Complicated; Use Everyday Language Instead
AI Overviews like content that sounds like it was written for people, not for computers. Models can better understand meaning when the words are simple, the transitions are smooth, and the phrasing is conversational. Strangely, the more a page tries to sound “optimised,” the harder it is for AI to understand.
[3] Add Examples or Situations From the Real World
A page is easier to remember when it feels like it comes from real life. AI systems can figure out context and intent even from a short story or a normal situation. Readers stay interested, and AI learns more about how the information works in real life.
[4] Put Together Information Without Making the Page Look Like a Checklist
AI Overviews like structure, but not formatting that is too strict or mechanical. Scanning models can find important ideas without getting confused by autogenerated fluff if there are gentle subheadings, a few lists where needed, and paragraphs that breathe. A layout that moves at a good speed makes it easier for both people and AI to follow.
[5] Use Specific Words Naturally, Not Stuffed
Putting relevant phrases in the right places helps AI figure out what the page is about, but too much repetition can make a page feel forced. Let keywords show up in a way that sounds like a real conversation. AI is more likely to understand the topic when the language flows.
[6] Keep Facts Up to Date and Only Use Them When They Really Help
AI Overviews get their information from sources that seem reliable and current. Adding recent statistics, timely observations, or a quick link to a source can quietly boost a page’s credibility. It doesn’t have to sound like a school paper; it just has to be accurate enough that both people and AI can tell it’s reliable without being hit over the head with it.
How Generative AI Is Changing Search Intent
Search intent is changing in ways that seem a little crazy but also more natural. People aren’t typing in neat, one-size-fits-all questions anymore. Instead, they’re throwing generative AI into very specific situations and expecting it to figure everything out all at once. GEO nuance, constraint-based comparisons, mid-conversation pivots, and layers of personal context all come together to change how SEO and SXO (Search Experience Optimization) teams think about what a “search” is. Instead of big groups and predictable funnels, intent now moves through small questions, real-life situations, and changing needs that come up as the user talks.
[1] Micro-queries Are Becoming More Common
People aren’t searching in general terms anymore; they’re looking for very specific situations that traditional SEO didn’t really take into account. Instead of “best local SEO tools,” people are now asking things like “best GEO tool for a local plumber in a flood-prone suburb.” Generative AI makes this easier because users can talk about specific problems instead of using keywords. People are starting to search for more specific problems instead of just browsing by category.
[2] Intent Seems More Situational Than Transactional
Search journeys used to follow neat boxes, like informational, navigational, and transactional. But generative answers change these lines. One question can show you how much money someone has, how they like to work, and even how much technical jargon they can handle. SXO teams are already making changes by linking content to situations instead of just funnel stages. It’s a mess, but it shows how people really think when they try to fix things in the real world.
[3] Before You Click Anything, Add More “Context Stacking”
Users don’t have to switch between five tabs; instead, they let AI add context right in the chat window. They improve questions like “Okay, but what if the store uses Shopify and has shipping zones that aren’t always the same?” And the model figures out the whole answer again. Websites only get clicks now when they add something that is uniquely trustworthy, like data, visuals, or firsthand experience. Everything else is handled in the conversation layer.
[4] Local and GEO-Focused Queries Are Sharper Than Ever
Generative AI doesn’t just look at where something is; it also reads the details around it. People type things like “quiet café in Lisbon that won’t glare at remote workers on Thursdays,” which is a lot more complicated than just “cafés near me.” Brands now need to know about micro-contexts like crowd patterns, weather habits, and neighbourhood quirks in order to do GEO. This depth shapes search intent in a way old keyword lists couldn’t predict.
[5] Comparing Prices is Becoming More Like Searching Based on Constraints
Instead of looking through “top 10 X tools,” users give AI a messy wishlist with things like tight budgets, unusual use cases, stubborn software integrations, and fringe preferences. Generative systems then choose options based on limits instead of how popular they are. SEO content needs to show this kind of behavior with specific examples, not just flashy lists of features.
[6] Search Intent Can Now Change During a Conversation
In a chat-style search, users change their minds quickly. One minute, they’re asking about analytics for a blog, and the next, they’re asking if the setup works for small teams that don’t have any technical staff. Search intent changes all the time, and AI changes with it. This means that brands need content clusters that can handle these changes. The best sites are the ones that give users layered information that they can “grow into” instead of just skimming it once and forgetting about it.
Why Conversational Queries Are Increasing
People are asking more conversational questions because they don’t want to have to sift through long, generic results when they just want an answer that fits their needs at that exact moment. People used to type stiff, keyword-heavy phrases into search engines, but now they ask them questions like they would ask a coworker or friend. This is especially true when the question is very specific, like how to find a laptop that won’t overheat during long video calls or a shampoo that won’t irritate a flaky scalp and works in hard water. Voice assistants and chat interfaces have made people speak more naturally, and once that becomes a habit, it feels awkward to go back. People also expect search tools to “get it,” even if the question isn’t fully formed or goes on for a while. As everyday problems become more specific, the language people use naturally follows, becoming more casual and complicated, like the way real thoughts sound.
Generative Engine Optimization (GEO): The New Face of Visibility
GEO seems like learning a new accent in a conversation you thought you already knew how to do. ChatGPT and Perplexity are not just link lists; they also figure out what you mean, and sometimes that meaning comes out in strange, almost messy micro-queries like “Which budget laptop can handle three Chrome profiles without melting?” Brands and creators need to make content that answers those oddly real questions, not just the polished ones we wish people would ask, if they want to stay visible in that world. GEO makes you think about how an AI model takes in context, hints, and half-formed thoughts, and then chooses what to show. It’s less about tricking an algorithm and more about being truly helpful in the kinds of everyday situations that people don’t often talk about how hard they are.
Strategies to Survive in a Zero-Click Search Environment
[1] Make Content Based On Very Specific, Slightly Messy Questions
People used to search for “best laptop,” but now they look for things like “laptop that doesn’t overheat during Zoom calls” or “printer that only smudges on glossy paper.” Pages that directly answer these small questions get clicks because the search snippet doesn’t fully explain the nuance. Specificity shows that the page really gets the issue.
[2] Write Answers That Stand On Their Own But Still Have Something Worth Clicking On
Summaries with no clicks: Get the obvious information, and the value must be in what is too detailed to get. The page stays useful even after the snippet ends with small fix-it steps, edge-case notes, or other paths. When people think there’s more than just the one-line answer that Google shows, they tend to open pages.
[3] Include Examples or Pictures That Micro-Queries Depend On
A search engine can summarise text, but it has trouble with a quick diagram that shows why a cable hums only in certain light or a side-by-side of two very similar phone settings. These small visual cues often do a better job of solving niche problems than words alone, which makes the user want to see the whole page.
[4] Keep Sections Short So That Readers Can Quickly Find Their Strange Problem
People who use micro-queries scan, not browse. They can quickly find the scenario that fits their own because of the short sections, brief explanations, and scannable bits of insight. This makes the page seem like a useful tool instead of just another long article.
[5] Make the Writing Sound Like a Person, Not Like It Was Made For Snippets
Search engines turn generic text into their own summaries. Using natural language, like small quirks, conversational language, and real-life examples, helps the page stand out. People trust content that doesn’t seem like it was made just to please an algorithm.
[6] Give Small Actions That Happen Outside of the Search Result
People will leave the zero-click bubble if you give them downloadable checklists, quick tools, or short guides. These extras are most useful when they help someone fix a very specific problem, not a broad one.
Creating Content That Still Drives Clicks
In 2026, content that gets clicks isn’t about cramming in a lot of keywords or turning a simple idea into a 2,000-word post. People keep clicking on a page because it is clear, quick, and gives them the feeling that it really understands the messy situation they are in. People who are looking for “how to fix schema validation error in product markup after theme update” don’t want a motivational introduction. They want context, a quick screenshot-style explanation, and proof that other people had the same problem.
Content that gets clicks usually answers small questions without making the reader search for the answer, like they’re on a scavenger hunt. SERPs are showing more and more AI-generated summaries, so people only click if the snippet suggests that the full article has more details, steps, or examples that the summary can’t give. Case studies, comparison tables, troubleshooting for edge cases, and short opinionated notes are often better than generic “ultimate guides.” People click when they feel like they are in the real world.
Structured Data: The Quiet Backbone of AI Search
Structured data is what makes AI-driven search visible, even though no one talks about it. It’s funny that it feeds machines more than it feeds people, because when it works, users can see the benefits right away: richer snippets, clearer previews, and fewer wrong answers. Schema markup is a big part of how AI search engines figure out what a page is, not just what the text says. Product, HowTo, FAQ, BreadcrumbList, Organisation, and Review are no longer optional decorations. Without them, everything looks like a pile of brown boxes, and your content gets lost in the back. They work like labels in a warehouse. Websites that use well-structured schema all the time tend to show up more accurately in AI overviews and multimodal search. This is especially true for specific searches like “3-minute tutorial for resetting XYZ router model” or “restaurant near me with allergen-friendly menu.” A schema is just the background work that helps search engines put things together.
Essential Schema Types to Implement
Even when algorithms change, some schema types still matter:
- Use the Organisation or LocalBusiness Schema to make sure that your NAP is consistent, that you have sameAs links, social profiles, and brand credibility.
- Product Schema with information about offers, GTINs, review snippets, and availability that updates in real time.
- FAQ and HowTo Schema for conversational and step-by-step questions that AI assistants look at all the time.
- Article/BlogPosting Schema with full information about the publisher and author.
- VideoObject Schema for sites that show both video and text answers in the same result block.
- Event Schema for local listings, especially when performers, dates, or ticket availability change a lot.
Adding the markup isn’t enough; you also need to use the property correctly. When AI summarises your content, it often skips over it because of missing fields or incomplete data.
EEAT in 2026: Building Real Authority That Google Trusts
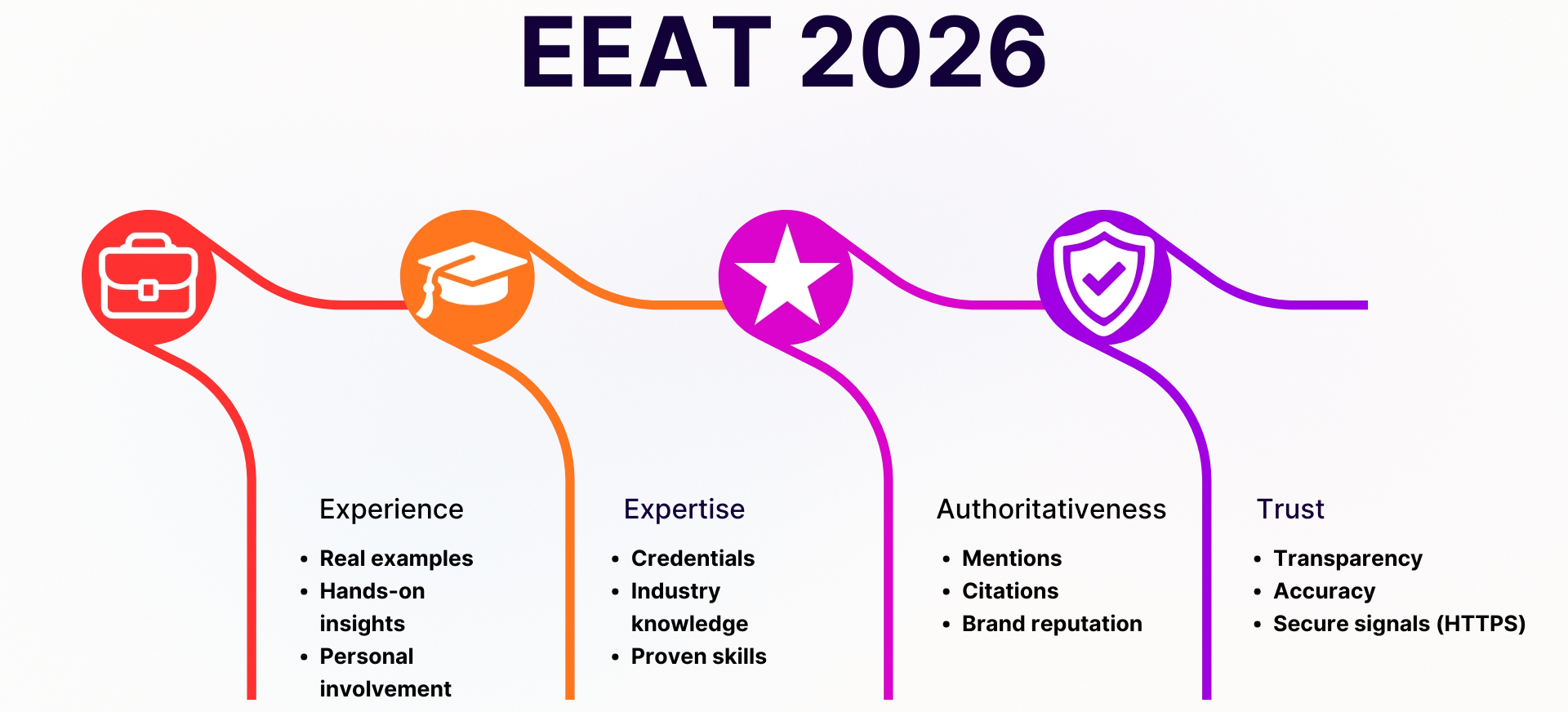
EEAT, which stands for Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trust, is no longer just a list. Search engines now look for patterns across whole ecosystems, such as who writes the content, who links to it, which communities talk about it, and how consistent the brand looks across the web. No more passing thin “expert” claims. Google and other search engines check credentials, publication history, and even social media presence against each other. The website with clear authorship, proof of experience, and clean trust signals almost always wins the ranking battle when two websites give the same advice.
How to Strengthen Your Brand’s Expertise and Trustworthiness
Websites are leaning more and more towards:
- Showing that you have experience, not just knowledge. Real-life examples, test data, and tools that were used in the process.
- Showing new ideas instead of just rehashing old ones.
- Keeping the same tone and quality of information across all categories.
- Keeping citations clean means using industry groups, scientific references, and well-known publishers.
When a website stops being anonymous, people trust it more. Brands that are easy to reach, have clear communication, and make it easy to find out about new content naturally build trust.
Author Profiles, Credentials, and Trust Signals
Strong author profiles include:
- Real credentials, like degrees, certifications, and awards.
- Statements of experience, like “worked with 80+ small businesses to fix schema and analytics.”
- Links to interviews, social media accounts, or contributions on sites that are known to be reliable.
- Revision dates, notes from the editor, and lists of sources.
More trust signals, like HTTPS, clear privacy terms, verified social pages, organisation schema, and correct NAP info, make the site more reliable overall.
User Intent Optimization: Capturing Micro-Queries and Conversational Search
People don’t just look for general topics anymore. They ask for strange, sometimes chaotic situations:
- “Why does my washing machine beep twice after draining only when it’s on eco mode?”
- “How do you compare two ETFs that are similar but track the same index?”
- “Which travel adapter will work in Japanese hotels with old wiring?”
Content that includes these small goals does better. Because conversational search engines read more like a friend giving advice, your content needs to be direct, contextual, and aware of edge cases.
Matching Content Types to the Right Intent
Not all intentions fit with a blog post. Some fit:
- Short charts for comparison
- Quick FAQs in mini-guides
- Troubleshooting flows
- Tools or calculators
- Walk-throughs with pictures
Questions for information need to be clear and well-organised. People who are looking to buy something often need help making a decision instead of ads. Transactional intent likes product pages that can be scanned and have changing data. Intent misalignment is one of the quiet ranking killers.
Optimizing for Visual, Voice, and Multimodal Search
Visual search usually looks at the quality of the images, the accuracy of the alt text, the product schema, and the filenames that describe the products. Voice assistants like short, clear instructions that use “natural language” and go straight to the point. Text, images, videos, and structured data are all combined in multimodal search. If your brand only has one format, you might miss users who search in very different ways, like taking a picture of a broken part and asking, “What’s the exact replacement for this?”
Semantic Search & Topic Clusters: The Future of Content Optimization

Topic clusters have been around for a while, but semantic search made them necessary. Search engines now look for connections between ideas like setting up a router, fixing Wi-Fi problems, mesh networks, and signal interference. They also check to see if your site covers the whole ecosystem instead of just parts of it. Clusters give structure to that ecosystem, which helps both crawling and ranking.
How to Build Topic Clusters That Boost Rankings
A good topic cluster starts with a clear main idea and then goes into all the little things that users go through. A better cluster might have more than one “internet speed guide,” such as
- Why do upload speeds drop so much during cloud backups?
- Antennas on the router are pointing the wrong way
- Speed problems with certain devices, like iPhones, gaming consoles, and smart TVs
- When ISP throttling really happens
When you see patterns in support chats, Reddit threads, and YouTube comments that show real problems, not made-up ones, clusters grow.
Internal Linking Best Practices for Topic Authority
Internal links shouldn’t feel like they’re being forced or automated. It works best when:
- Links show up where a user might really think, “I wish I had a better explanation right now.”
- Anchor text talks about the idea in a natural way, not the exact keyword.
- Pillar pages link to subtopics, and subtopics link back to or across to other subtopics.
This method gives both crawlers and users a clear path instead of a maze of text.
Video & YouTube SEO: Capturing Attention in 2026
Not only did video become more popular, but it also became a main way to search. A lot of people would rather see how to do something than read about it, especially when it comes to fixing things, setting up tech, doing makeup, cooking, and using software. AI overviews now show YouTube results, so your video can rank even if your website doesn’t.
YouTube SEO Best Practices for 2026

In 2026, the basics look a little different:
- Titles that are based on problems, not summaries.
- Chapters that are easy to read and understand so that AI can use them in responses.
- Intros that keep people’s attention and get to the point quickly.
- In-depth descriptions with keywords, timestamps, and background information.
- Strong engagement signals, like comments, likes, and rewatches, are still important.
- Adding the VideoObject schema to your site can help you prove that you own it.
- Short videos are great for quick fixes, but long videos are still the best for searches that are based on tutorials.
How to Rank Videos on Google Search
To get a good ranking on Google, you need:
- Adding structured data to related pages that have videos.
- Using descriptions that are rich in transcripts because AI crawlers depend on text a lot.
- Matching the search intent: For example, a step-by-step repair guide needs to go slower and have close-up shots.
- Clear thumbnails that show what the problem is and how to fix it.
Google combines AI answers with video, text, and images. The more signals you give, the more visible you will be.
Link, Brand, and Local Nexus: Strategic Growth Pillars
Authority links, brand signals, and local SEO are more closely related than they used to be. A website that has a lot of links but a bad brand reputation doesn’t rule anymore. Search engines look for consistency, like consistent branding, local citations, and mentions in trusted ecosystems.
Why Authority Links Matter More Than Quantity
One link from a well-known government or industry website can be worth more than 100 low-quality directory links. Backlinks from high-authority sites usually come from content that is worth linking to, like data, case studies, tools, or strong opinions. Quantity-only link building often backfires, especially in AI-driven spam detection.
How Google Rewards Brand Authority
Search engines increasingly reward:
- Brand mentions across communities
- Consistent data about entities in Knowledge Panels
- Real users have good things to say about it
- Clear identity: logo, name, NAP, social profiles, structured Organization data
Brands that are seen as “entities” are easier to find, especially when searches are unclear.
Local SEO Best Practices in an AI-Driven World
Local search now depends on:
- Correct information about business hours and menus/catalogs
- Photo freshness (old photos often make people less interested)
- Look at the patterns of sentiment
- LocalBusiness schema with a price, range, and amenities area served fields
- Store-level content that answers hyperlocal questions like parking, accessibility, and peak hours
AI tools show summaries from reviews, so it’s more important to be real than to stuff keywords.
AI-Powered Keyword Research and Real-Time Trends
In 2026, keyword research isn’t about making lists; it’s about finding patterns. AI tools keep an eye on how people talk about problems, sudden spikes in niche problems, and small changes in how people talk about the same problem. Micro-trends show up quickly, especially on social media. Brands that spot them early make content that gets both freshness boosts and early authority.
How AI Improves Keyword Clustering & Intent Mapping
AI models find clusters by looking at how people ask questions, what they click on next, and which topics are related to each other. This helps to better understand what people want. For example, people who search for “best humidifier for baby room congestion” act differently than people who search for “humidifier vs air purifier for allergies.” AI picks up on these small differences and groups content accordingly.
Winning With Freshness and Trending Topics
It’s not enough to rewrite old articles every month to stay fresh. It’s about being aware of when something starts to gain traction, like new laws, new product launches, sudden failures in popular apps, viral cleaning hacks, or travel warnings in the middle of the season. Getting involved in these questions early on gives you authority that lasts long after the trend settles down.
Preparing Your Website for Sustainable Growth Beyond 2026
It’s not about guessing every algorithm update when you future-proof a site. It’s about making systems that are easy to change: clean architecture, structured data, strong EEAT signals, a variety of content formats, and navigation that puts the user first. Even when search trends change, websites with strong foundations usually do well.
Long-Term SEO Strategies and Future-Proofing
Long-term plans include:
- Keeping evergreen clusters up to date with regular reality checks.
- Making UX better all the time, loading time, ease of use, and clear navigation.
- Creating long-lasting brand recognition across all platforms.
- Fairly getting user data to learn about new needs.
- Making libraries of content in many formats, like text, video, tools, and images.
A future-proof site feels alive, not empty. Users can tell that someone is really paying attention.
How Next Olive Will Help Your Brand Rank Higher in 2026
Next Olive is different from other SEO companies because, being an experienced SEO services company, it has more than 13 years of real-world experience and a team of more than 200 professionals who know how modern AI-driven search works. The company has worked on more than 200 projects in more than 20 countries, giving them real-world experience with technical SEO, structured data, entity optimisation, and advanced keyword clustering. Their method combines research on predictive intent, content strategies that can grow, YouTube, and video SEO, and deep technical fixes like optimising Core Web Vitals, adding schema markup, and improving crawl architecture. Next Olive doesn’t just use surface-level tactics; it uses a full ecosystem strategy that helps brands grow in a way that lasts and stay visible in a competitive search landscape in 2026.
Conclusion: Getting Ready for the Next Era of Search After 2026
The main idea behind SEO in 2026 is that search engines now reward depth, clarity, and real authority. Structured data, EEAT, entity signals, multimedia content, semantic topic clusters, and intent-focused optimisation all work together to change how visible something is. Brands that change with AI-driven search, especially by having strong technical foundations, reliable content, and quick answers to new micro-queries, are the ones that keep their rankings. Websites that don’t just chase algorithms but also feel helpful will be the ones that last.
Frequently Asked Questions
Which is the best SEO services company close to me?
Next Olive comes up a lot when businesses compare local agencies. This is mostly because the team has been around for more than 13 years and has worked with clients in more than 20 countries. They usually have an advantage when it comes to unusual or very specific SEO problems because they have a lot of experience and have worked in a lot of different markets. This is especially true for the new “micro-query” behavior that will shape search in 2026.
Are search results made by AI killing regular SEO?
They are not getting rid of it; they are changing it. AI Overviews mostly show surface pages that have very specific information that most generic articles don’t include. Sites that offer these deeper, scenario-based insights are still around, but sites with thin content are pushed to the side. SEO is still around, but the rules have changed.
Is keyword research still helpful now that people search with full sentences?
Yes, very much so, but it feels different now. Instead of focusing on one “main keyword,” teams look for groups of real-world questions, like troubleshooting questions or very specific comparisons. In 2026, most organic traffic will be hiding in these longer, more detailed searches.
Will small websites be able to compete with big brands in 2026?
Yes, a lot more than people think. Big sites usually publish general, shiny overviews, while smaller sites look at specific use cases. That level of detail makes it easier for AI models and search engines to figure out how valuable the page is. On narrow but high-intent topics, small blogs often do better than big ones in the same field.
How important will page speed be in 2026?
Still important, but more about how the page looks and feels. A site doesn’t need to get a perfect score; it just needs to avoid little things that make reading hard, like slow scripts, moving images, and late-loading fonts. Search engines notice these small delays right away, which makes people leave quickly.
Are backlinks still important?
Yes, but the rule of “quality over quantity” has become stricter. A link from a small, very relevant site, like a niche community page or a technical blog, is often worth more for ranking than a link from a big, but not very focused, publication. Search engines now rely a lot on context.
In 2026, how much does user experience matter for SEO?
A lot. Instead of just design metrics, search engines look at behavior signals. If people scroll smoothly, find what they need, and don’t bounce back right away, the rankings usually show that. Without needing fancy effects, clean layouts, and easy-to-read writing tend to win.
Should content be written for people or for AI tools?
Writing for people is still the best way to do it. AI tools naturally pick up the useful parts when the content is clear, has real examples, and doesn’t have any filler. People and search engines often ignore pages made “for AI” because they sound vague or repetitive.
Next Olive comes up a lot when businesses compare local agencies. This is mostly because the team has been around for more than 13 years and has worked with clients in more than 20 countries. They usually have an advantage when it comes to unusual or very specific SEO problems because they have a lot of experience and have worked in a lot of different markets. This is especially true for the new “micro-query” behavior that will shape search in 2026.
They are not getting rid of it; they are changing it. AI Overviews mostly show surface pages that have very specific information that most generic articles don’t include. Sites that offer these deeper, scenario-based insights are still around, but sites with thin content are pushed to the side. SEO is still around, but the rules have changed.
Yes, very much so, but it feels different now. Instead of focusing on one “main keyword,” teams look for groups of real-world questions, like troubleshooting questions or very specific comparisons. In 2026, most organic traffic will be hiding in these longer, more detailed searches.
Yes, a lot more than people think. Big sites usually publish general, shiny overviews, while smaller sites look at specific use cases. That level of detail makes it easier for AI models and search engines to figure out how valuable the page is. On narrow but high-intent topics, small blogs often do better than big ones in the same field.
Still important, but more about how the page looks and feels. A site doesn’t need to get a perfect score; it just needs to avoid little things that make reading hard, like slow scripts, moving images, and late-loading fonts. Search engines notice these small delays right away, which makes people leave quickly.
Yes, but the rule of “quality over quantity” has become stricter. A link from a small, very relevant site, like a niche community page or a technical blog, is often worth more for ranking than a link from a big, but not very focused, publication. Search engines now rely a lot on context.
A lot. Instead of just design metrics, search engines look at behavior signals. If people scroll smoothly, find what they need, and don’t bounce back right away, the rankings usually show that. Without needing fancy effects, clean layouts, and easy-to-read writing tend to win.
Writing for people is still the best way to do it. AI tools naturally pick up the useful parts when the content is clear, has real examples, and doesn’t have any filler. People and search engines often ignore pages made “for AI” because they sound vague or repetitive.




